Understanding Vocal Anatomy for Better Singing
Have you ever thought about what happens in your body when you talk or sing? It’s amazing how the vocal cords, larynx, and diaphragm work together. This knowledge helps us appreciate our voices more and take better care of them.
The Role of the Diaphragm in Voice Production
The diaphragm is a key muscle in the body. It helps a lot in making sound. Learning to use it well can make your singing better. It helps with breath support and vocal performance.
The Diaphragm’s Anatomy
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle below the lungs. It flattens when you breathe in. This action pulls air into your lungs.
This movement is what’s controlling air flow in your singing.
How the Diaphragm Affects Singing
In singing, the diaphragm helps with steady breath support. This is important for keeping notes steady, controlling volume, and keeping pitch right.
Singers who use their diaphragm well can make their voices sound stronger and clearer. This also helps them sing longer without getting tired. It also protects their vocal cords from getting hurt.
Anatomy of the Larynx: The Voice Box
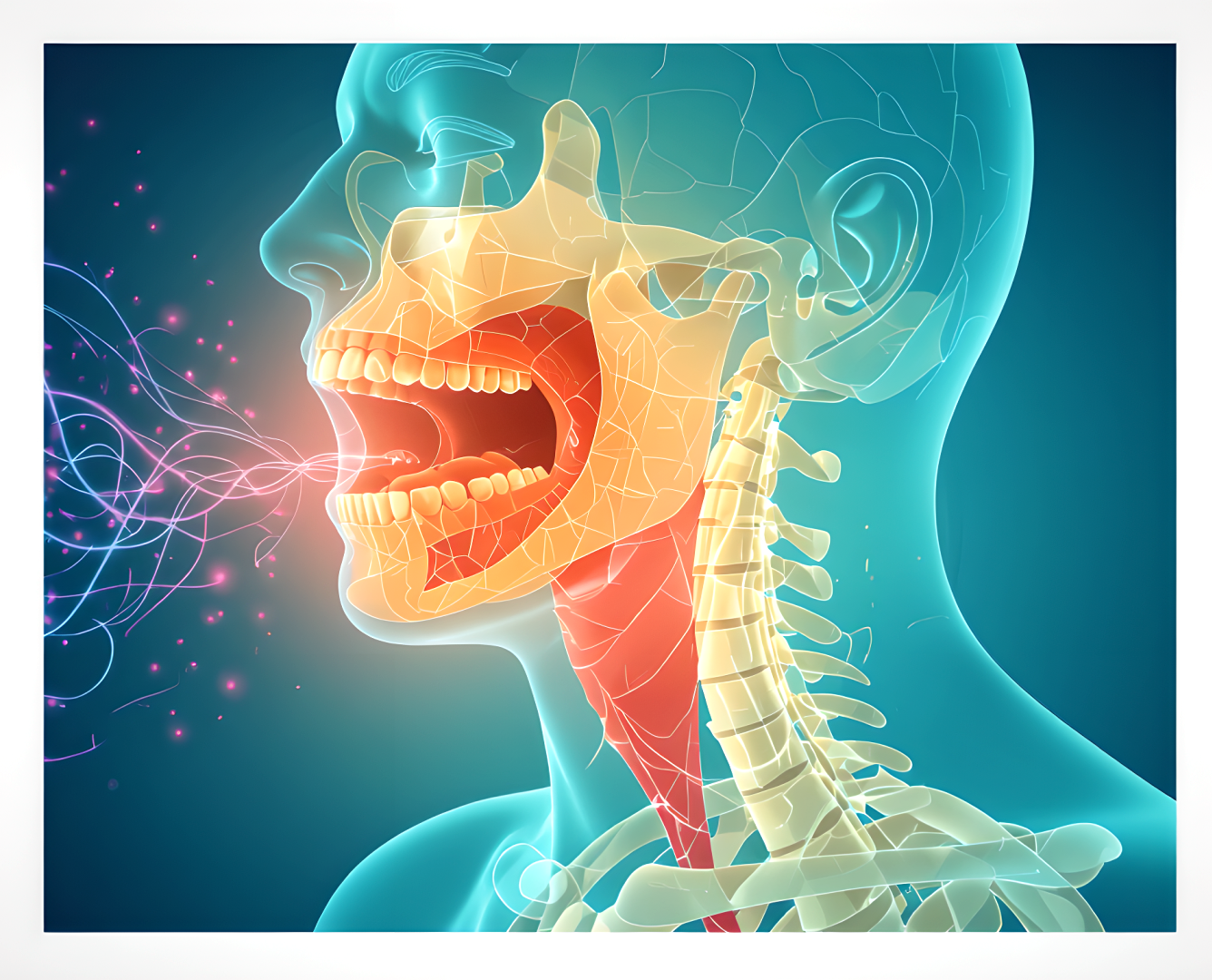
The larynx, also known as the voice box, is what produces sound. It’s in the throat and helps with breathing and protecting the airway. It’s made of cartilage and muscles that work together.
Key Cartilages in the Larynx
In the larynx, you’ll find important cartilages. The thyroid, cricoid, and arytenoid cartilages are the main ones. They help the voice box move and change sound.
Each cartilage has a special job. They help with sound and keep the airway safe.
Muscles Involved in the Larynx
The larynx has many muscles. These muscles help the voice box move and change sound. They work together to make your voice sound different.
These muscles help you change your voice’s pitch, volume, and quality. This lets you express yourself better.
Vocal Cords vs. Vocal Folds: What's the Difference?

Understanding the difference between vocal cords and vocal folds
Structure of Vocal Folds
The vocal folds are in the larynx. They are made of muscles and tissues. These parts are vital for making sound waves.
When you talk or sing, your vocal folds vibrate. These vibrations create the sound waves. These waves are what let us express our voice.
Function of Vocal Cords in Sound Production
“Vocal cords” is a term for a part of the vocal folds. These cords help control pitch and voice changes. They do this by changing how they vibrate.
As air goes through the closed vocal folds, they make different sound waves. These sound waves change the voice’s quality.
The Importance of the Respiratory System in Singing
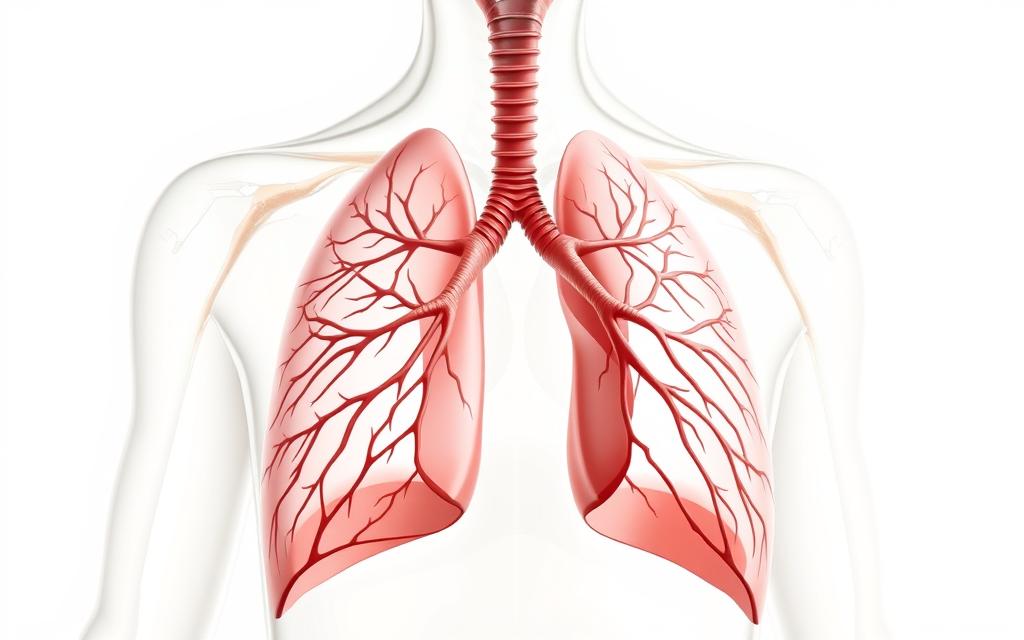
The respiratory system is key in singing. It affects how well you sing and how strong your voice is. This part explains how the lungs, intercostal muscles, and abdominal muscles help you sing better.
Role of the Lungs
Your lungs help make sound by providing air and pressure. Deep breaths and good exhalation help you sing long and strong notes. Singers need to control their breath well. This keeps your tone steady and prevents vocal strain.
Intercostal and Abdominal Muscles
The intercostal muscles are between your ribs. They help your chest expand and contract when you breathe. These muscles, with the diaphragm and abdominal muscles, help control your breath. This lets you change your voice easily. Exercises to strengthen these muscles can improve your singing.
How Vocal Folds Vibrate to Produce Sound

Vocal fold vibration
Then, air from your lungs pushes through these closed folds. They start to vibrate fast, making sound waves. These sound waves are what we hear as your voice.
The way your vocal folds vibrate affects your voice. If they’re tight, your voice sounds harsh. But if they’re relaxed, your voice is softer and sweeter.
But making sound is more than just vocal fold vibration. The diaphragm, lungs, and other parts also play a big role. They work together to make your voice sound better and louder.
By learning how these parts work together, you can control your voice better. This leads to a more polished and clear sound.
The Concept of Resonance in Vocal Production
Understanding resonance
What Are Vocal Tract Resonators?
Vocal tract resonators are the areas where your voice gets louder. They include your chest, pharynx, mouth, and nose. Each one adds a special touch to your voice, letting you create different sounds.
The Role of the Pharynx, Mouth, and Nasal Cavities
The pharynx, mouth, and nose are very important for your voice. The pharynx changes shape to change your voice sound. The mouth affects how your voice sounds and helps with different sounds.
The nose adds a special sound to your voice. It makes your voice richer and more powerful. This is because sound resonates in your face’s bones and tissues.
Understanding Vocal Anatomy
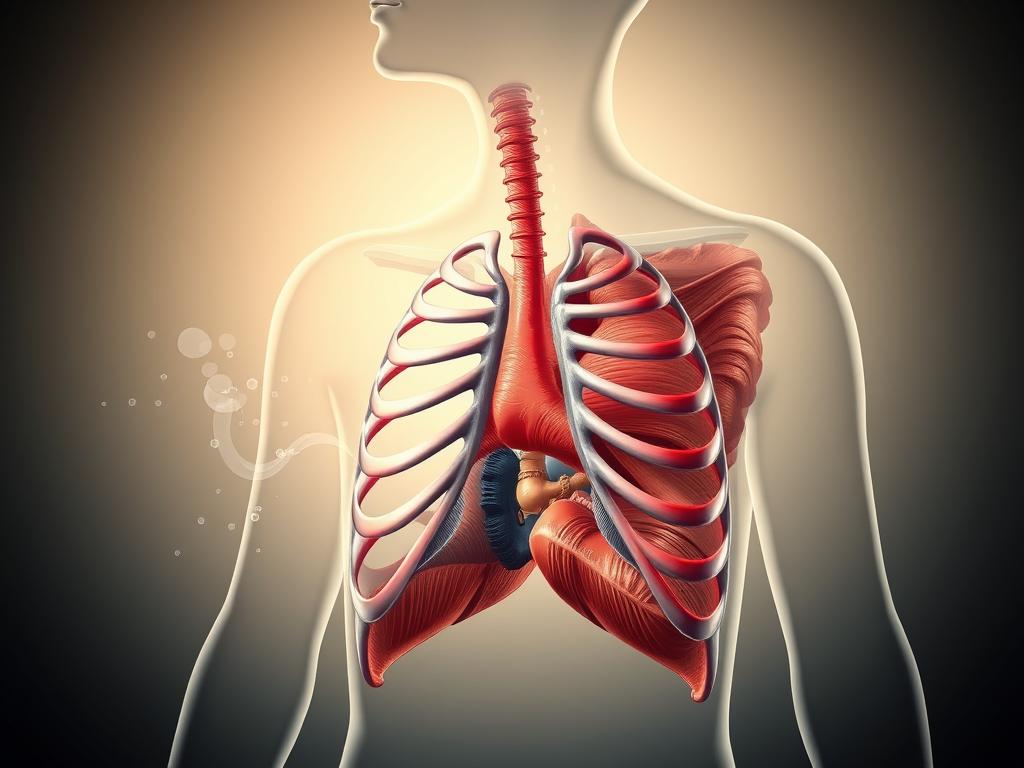
Knowing vocal anatomy
The larynx, or voice box,
Singing techniques depend a lot on the laryngeal anatomy. For example, learning to control your vocal folds helps make your sound more consistent and strong. Also, knowing how to use your diaphragm and breathing system improves your breath control and how long you can sing.
Keeping your voice healthy is very important, whether you sing for work or just for fun. Knowing about vocal anatomy helps you use your voice safely and for a long time. Things like warm-ups, staying hydrated, and careful practice can make your voice last longer and sound better.
The Glottis: The Gateway of Sound

The glottis
Function of the Glottis in Breath Control
The glottis controls your breath by opening and closing. It lets the right amount of air through when you speak or sing. This helps you keep your voice steady and clear.
Role of the Glottis in Sound Production
The glottis also makes sound happen. Air passing through makes the vocal folds vibrate. This is how you change pitch and volume. Learning to control your glottis makes your voice better.
Dynamics of Voiced Sound: Pitch, Volume, and Quality
Understanding voiced sound dynamics is important for a great vocal performance. Voice dynamics cover changes in loudness and how you control them. This helps show emotions and meaning well.
Getting better at pitch control is vital for singing and speaking correctly. Keeping your pitch steady makes your voice clear and interesting.
Sound quality is also very important. It’s about how clear, warm, and full your voice sounds. To get better sound, work on your breathing, keep your throat relaxed, and use your mouth and throat well.
Managing your vocal intensity is also important. It helps avoid voice strain and keeps your voice strong. Using your breath and diaphragm right helps control your voice well.
Common Voice Disorders and Their Connection to Vocal Anatomy
It’s important to know about common voice disorders and how they relate to vocal anatomy. These issues can harm your vocal health. Problems like vocal cord damage and laryngeal nerve dysfunctions are common. Understanding these can help you keep your voice healthy.
Vocal Cord Lesions
Vocal cord lesions can make it hard to speak or sing. These include nodules, polyps, and cysts. They often happen from using your voice too much.
Damage from these lesions can cause hoarseness or a change in voice pitch. It might even lead to losing your voice. To avoid this, do warm-ups before speaking or singing. Also, try not to shout too much.
Nerve Disorders Affecting Voice
Laryngeal nerve dysfunctions can also cause voice problems. These nerve issues can come from surgery, trauma, or viruses. They can make your vocal cords move poorly.
You might have a breathy voice when your vocal cord nerves are affected. You could also feel vocal strain or have trouble projecting your voice. Getting medical help quickly is key to fixing these problems and keeping your voice healthy.
The Physiology of Phonation

Understanding how your voice works is key. Phonation is when air moves through your vocal cords to make sound. The muscles in your larynx and vocal cords work together to create your voice. This shows how amazing it is to make sounds.
Your lungs start by making air flow. This air goes up through your trachea and reaches your larynx. Here, the vocal cords vibrate to make different sounds.
The way your vocal cords vibrate changes your voice’s pitch and volume. This is because of how they are set up. It’s a complex process, but it’s natural for many people. This shows how amazing our bodies are at making sounds.
The Role of Articulators in Speech and Singing
Understanding the speech organs is key to clear vocal articulation. Both movable and fixed articulators are important. They help produce sound and ensure clear speech.
Movable Articulators: Lips, Tongue, Soft Palate
The lips, tongue, and soft palate are vital. They shape sounds and help with precise vocal articulation. Their flexibility makes singing clearer and better.
Fixed Articulators: Hard Palate, Teeth
The hard palate and teeth are fixed articulators. They offer stable surfaces for the movable ones. They are essential for clear diction and sound quality in speech and singing.
The Impact of Muscle Tension on Vocal Quality
Understand how muscle tension affects your voice. Tension in the neck and laryngeal muscles can cause vocal strain. This strain makes it hard to sing clearly and with good resonance.
When muscles around your vocal cords are tight, they limit movement. This makes controlling pitch and volume harder. It’s important to relax your jaw, neck, and shoulders.
Practicing healthy singing means relaxing and using good breath support. Techniques like the Alexander Technique help you feel and release tension. This leads to easier and more natural singing.
Being aware of muscle tension and its impact on your voice is vital. Regular exercises that focus on relaxation and breath control help. This way, you can sing with a richer sound and avoid long-term damage to your voice.
Improve your Singing in 30 Days

Join Our Singing Community
Become a part of the Singing Community and gain access to exclusive resources and expert guidance on vocal techniques. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned performer, our community offers support and inspiration to help you reach your vocal potential.

